Personalized LLM-Based Smart Home Assistant
Human-Robot Interaction
Collaborator(s): Precious Philip-Ifabiyi, Atharva Patwe, Mohamed Khaled
This project proposes a robust framework that combines these capabilities with the TIAGo robotic platform to create a personalized home assistant robot. By leveraging OpenAI Whisper, ChatGPT 4o, and ElevenLabs, the system aims to enable seamless interactions between humans and robots, facilitating context-aware tasks and adaptability in dynamic home environments.
The significance of this work lies in addressing challenges such as accurate natural language understanding, adaptive task planning, and efficient execution of robotic actions. By integrating ROS as the underlying framework, the proposed system ensures modularity and scalability, enabling the TIAGo robot to perform a wide range of tasks, from conversational interactions to practical operations like pick-and-place.
Methodology
Simulation Environment
The experimental environment for this project is a simulated small house, designed to emulate realistic conditions found in home settings. This environment, provided by the AWS Robomaker Small House World, is used to test the robot’s navigation, object manipulation, and human interaction abilities.
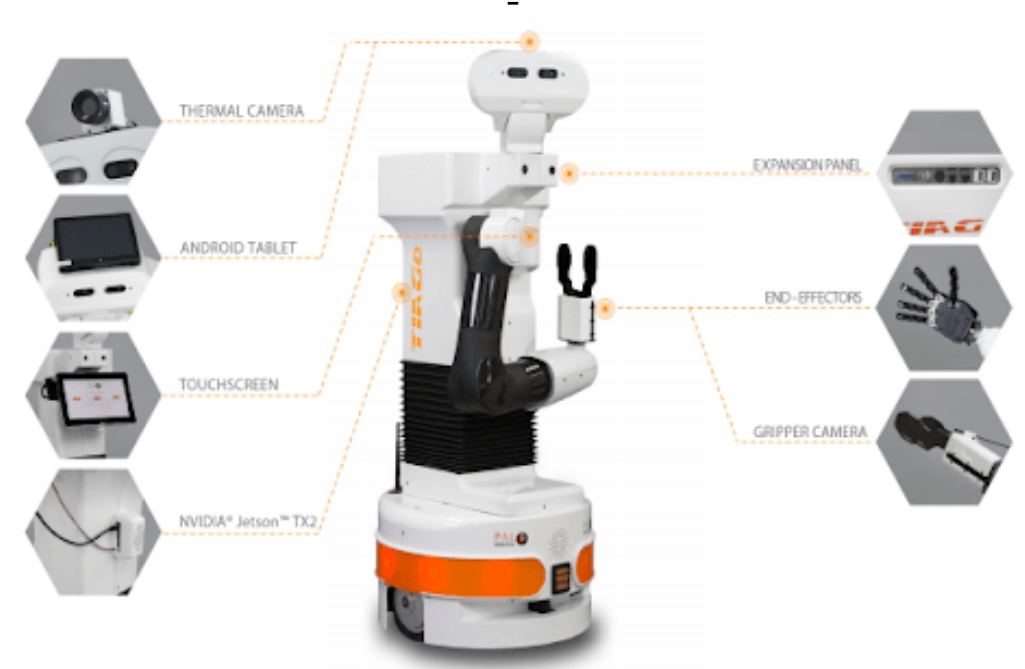


Effective Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) is a crucial component of this project, enabling intuitive and natural communication between users and the TIAGo robot. The following subsections detail the key HRI methodologies employed:
- Voice Command Interaction
- Robot Voice Response
- Gesture-Based Feedback
- Socially Aware Interaction
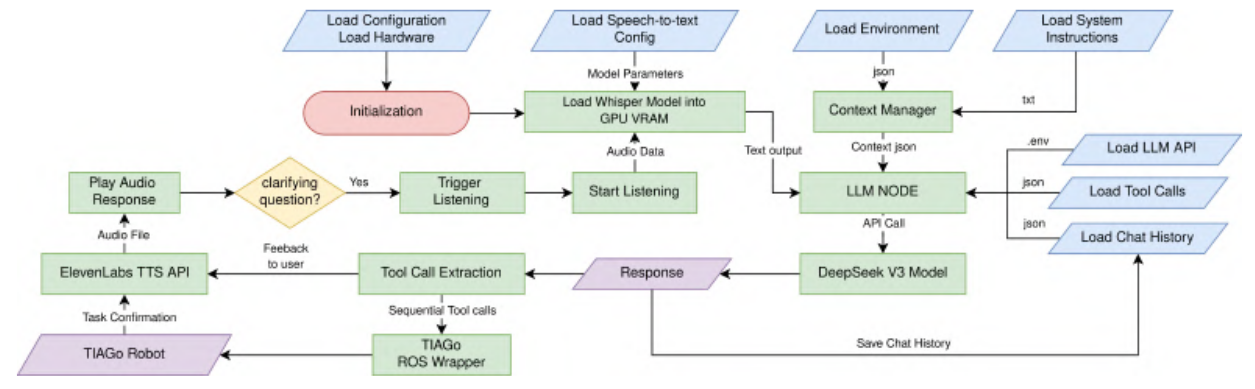
LLM Input
The input to the LLM system is derived from user speech, which is processed using OpenAI Whisper. Whisper transcribes spoken language into text, serving as the input prompt to the LLM node. This transcription ensures accurate conversion of voice commands into actionable textual instructions that can be further processed.
LLM Node
The LLM Node is the core component that processes input text and determines appropriate robotic actions. This node is divided into several key components:
- Context: The system maintains an understanding of the environment through a JSON file. This file contains:
- Object locations and their properties
- Room layouts and positions
- Mapping information for navigation
This environmental context enables the LLM to make informed decisions based on spatial awareness.
- System Prompt: The system prompt defines the robot’s identity, capabilities, and constraints. The robot, named Tiago, operates with the following specifications:
- Mobile manipulator with a single arm
- ROS-based movement and control
- Safe velocity limits (1.0 m/s linear, 1.0 rad/s angular)
- Interaction via natural conversation
- Execution of predefined motion sequences
The prompt also outlines interaction guidelines, including safety considerations, task execution constraints, and clarifying queries when instructions are ambiguous.
-
Tool Calls: The system employs a structured set of atomic actions and conversation responses.
a. Robot Atomic Actions: Atomic actions are fundamental operations that enable complex tasks. These include:
- Publish command velocity - Direct velocity commands for movement.
- Move to point - Navigate to a specific location.
- Pick object - Pick up objects.
- Execute motion - Perform a predefined movement pattern.
- Speak to user - Generate verbal feedback.
- Place object - Places objects at a designated position.
These atomic actions can be composed to execute complex behaviors, facilitating reusability and extensibility. The system allows for additional user-defined atomic actions through imitation learning.
b. Conversation Response: Apart from physical actions, the LLM can generate conversational outputs. These include:
- Providing answers to user queries
- Requesting clarification when the input is ambiguous
- Resuming active listening after incomplete instructions
- Chat History: To ensure contextual continuity, the system maintains a record of previous interactions. This chat history allows the LLM to:
- Reference prior user commands
- Maintain task context across multiple exchanges
- Improve response relevance based on past inputs
LLM Output
The final stage involves executing the LLM’s output through two primary modalities:
- Conversation Output: To enable seamless interaction, the generated text response is converted into speech using ElevenLabs’ text-to-speech synthesis. This ensures natural, vocalized feedback for users.
- LLM Robot Action Output: For physical execution, the LLM translates its decisions into ROS-compatible commands. These commands may involve motion planning, object manipulation, or predefined gestures. The execution follows safe operation constraints and real-world feasibility checks.
Results
-
Long-Horizon Task Execution
The ability of the system to perform long-horizon tasks, which require sequential execution of multiple atomic actions, was also evaluated. In one scenario, a book was placed in the environment, and the robot was prompted to ”fetch the book and bring it to the living room”. To successfully execute this task, the robot needed to navigate to the location of the book, pick it up, and transport it to the living room. The robot completed these steps autonomously without requiring additional context.
Similarly, another task involved placing a banana on the dining table and prompting the robot with ”Can you bring the banana and place it in the living room?”. Leveraging contextual knowledge about the banana’s location, the robot autonomously navigated to the dining table, picked up the banana, transported it to the living room, and placed it appropriately. These results demonstrate the model’s capability to plan and execute complex tasks based solely on high-level user instructions.
-
Comparison of Different Large Language Models The performance of different LLMs was compared using identical task prompts. Two models were evaluated: DeepSeek V3 from DeepSeek and OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4o. The DeepSeek V3 model demonstrated superior performance in handling sequential and long-horizon tasks compared to ChatGPT-4o. For instance, when prompted to ”bring the banana to the living room”, ChatGPT-4o occasionally failed to execute the pick action after navigating to the banana’s location.
Various prompt modifications, such as using ”fetch” instead of ”bring,” did not significantly improve ChatGPT-4o’s performance in this context. Conversely, DeepSeek V3 did not exhibit this issue, consistently executing the correct sequence of actions. This suggests that DeepSeek V3 has a more robust understanding of task planning in a home-assistant robotics context.
Impact and Future Work
This study presents a personalized LLM-based smart home assistant using the TIAGo robot, leveraging OpenAI Whisper for speech recognition, ChatGPT-4o for reasoning, and ElevenLabs for speech synthesis. The system successfully demonstrated its ability to interpret and execute both atomic and long-horizon tasks, ensuring a seamless interaction experience with users.
While certain simplifications were employed, such as the use of a predefined JSON file for specifying room and object locations, the system showcases significant potential in improving human-robot interactions in home environments. Experimental evaluations confirmed its effectiveness in executing complex commands autonomously and adapting to user interactions.
Future work will focus on enhancing task execution efficiency, improving semantic world understanding through deep learning models, and advancing personalization features to create more adaptive and intuitive home assistant robots. These improvements aim to further bridge the gap between human intent and robotic execution in real-world applications.